OverviewBenign prostate enlargement
Benign prostate enlargement (BPE) is the medical term to describe an enlarged prostate, a condition that can affect how you pass urine.
Symptoms of benign prostate enlargement
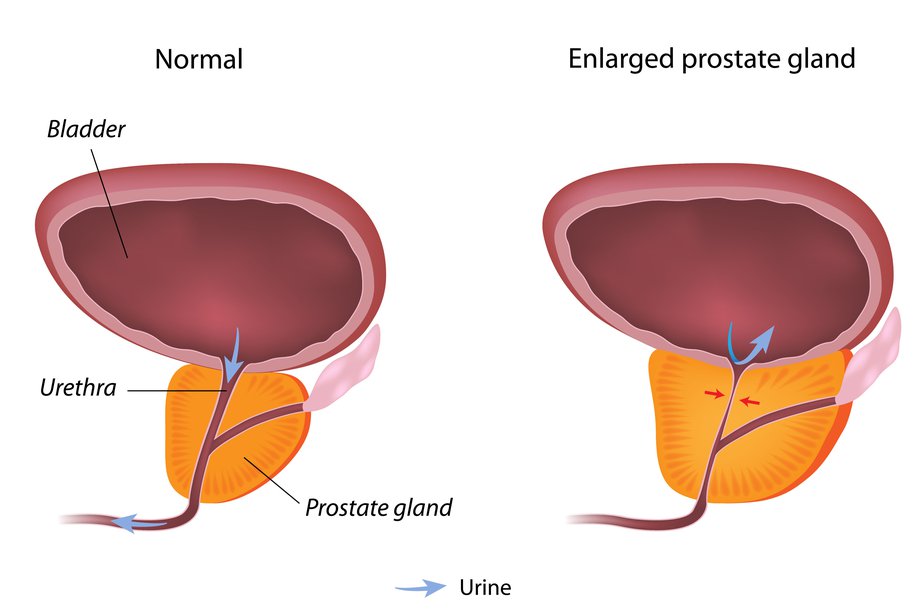
The prostate is a small gland, located in the pelvis, between the penis and bladder.
If the prostate becomes enlarged, it can place pressure on the bladder and urethra (the tube through which urine passes).
This can affect how you pee and may cause:
- difficulty starting to pee
- a frequent need to pee
- difficulty fully emptying your bladder
In some men, the symptoms are mild and don't need treatment. In others, they can be very troublesome.
Read more about the symptoms of benign prostate enlargement.
Many men worry that having an enlarged prostate means they have an increased risk of developing prostate cancer. This isn't the case.
The risk of prostate cancer is no greater for men with an enlarged prostate than it is for men without an enlarged prostate.
Causes of benign prostate enlargement
The cause of prostate enlargement is unknown, but it is believed to be linked to hormonal changes as a man gets older.
The balance of hormones in your body changes as you get older and this may cause your prostate gland to grow.
Media last reviewed: 22/01/2018
Media review due: 22/01/2021
Diagnosing benign prostate enlargement
You might have several different tests to find out if you have an
enlarged prostate.
enlarged prostate.
Your GP may do some of these tests, like a urine test, but others might need to be carried out at a hospital.
Some tests may be needed to rule out other conditions that cause similar symptoms to BPE such as prostate cancer.
Read more about diagnosing benign prostate enlargement.
Treating benign prostate enlargement
Treatment for an enlarged prostate will depend on the severity of your symptoms.
If you have mild symptoms, you won't usually need immediate treatment but you'll have regular prostate check-ups.
You'll probably also be advised to make lifestyle changes, such as:
- drinking less alcohol, caffeine and fizzy drinks
- limiting intake of artificial sweeteners
- exercising regularly
- drinking less in the evening
Medication to reduce the size of the prostate and relax your bladder may be recommended to treat moderate to severe symptoms of BPE.
Surgery is usually only recommended for moderate to severe symptoms of BPE that have failed to respond to medication.
Read more about treating benign prostate enlargement.
Complications of prostate enlargement
Benign prostate enlargement can sometimes lead to complications such as:
- urinary tract infection
- acute urinary retention
Acute urinary retention (AUR) is the sudden inability to pass any urine.
Symptoms of AUR include:
- suddenly not being able to pee at all
- severe lower abdominal pain
- swelling of the bladder that you can feel with your hands
Go immediately to your nearest accident and emergency (A&E)department if you experience the symptoms of AUR.